Diabetes is one of the fastest-growing health conditions worldwide and a leading cause of blindness in working-age adults in the United States. Diabetes is a complex metabolic disorder in which your body doesn’t produce enough insulin, resulting in excess blood sugar in the body. High blood sugar levels can affect various organs, including your eyes, and cause poor vision and even blindness.
Having type 1 or 2 diabetes means you can suffer short-term and long-term eye complications. Short-term eye complications include blurriness, which resolves when the blood sugar level falls to normal levels. In comparison, long-term complications occur when abnormally high blood sugar levels damage your eye’s blood vessels and retina.
Blurry Vision
Blurry vision is a first warning sign of progressive vision impairment due to diabetes. Blurry vision occurs when fluid leaks into the lens and makes your eyes swell and change shape. Swelling and change in shape make your eye lose its ability to focus, and things appear blurry. Controlling your blood sugar level and bringing it to be normal can help your eyes get back to normal.
Cataracts
A cataract is a condition in which the lens of your eye becomes cloudy. Diabetes is a common cause of having cataracts at a young age. The eyes lens contains an enzyme called sorbitol dehydrogenase. The accumulation of this enzyme in the eye makes your lens opaque, causing blurry vision.
Your eye doctor may recommend cataract surgery to remove the cataract.
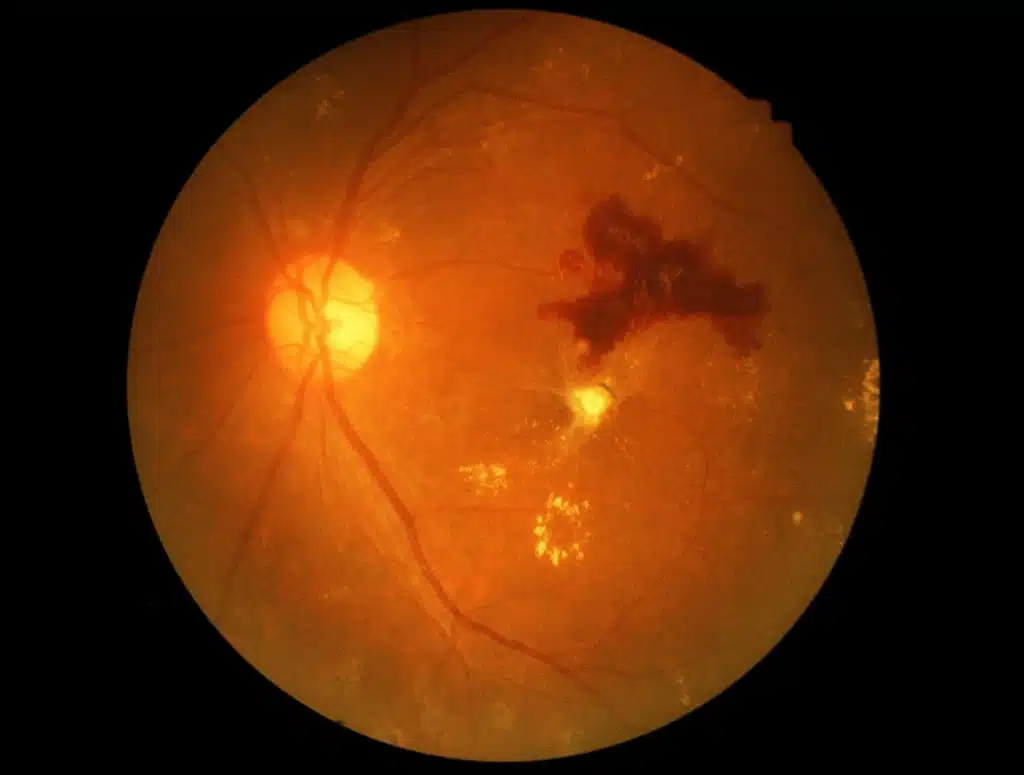
Diabetic Retinopathy
The retina is in the back of the eye. It takes in light and convert it into signals, which are sent through the optic nerve into the brain. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels of the retina. These damaged blood vessels leak fluid or blood (hemorrhage), resulting in problems with vision, scarring, and loss of retina cells.
Keeping your blood sugar level in a normal range can reduce your chances of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a common problem, and nearly 3 million people are affected by it in the United States. Glaucoma occurs when eye fluid can’t drain and pressure builds up inside the eye. The high pressure damages the optic nerve, blood vessels, and changes vision. The longer you suffer from diabetes, the higher your risk of developing glaucoma.
Medications can treat glaucoma by lowering eye fluid pressure, increasing fluid drainage, and reducing the production of fluid in the eyes.
Macular Edema
The macula of the eye is located near the retina’s center and is responsible for sending high-resolution images to the brain. The macula is essential for crisp vision. With diabetic retinopathy, macular edema can occur, resulting in a vision-related problems, such as fuzzy or wavy vision.
Eye Doctor for Diabetes Near Me in Greater St. Louis, MO
If you have diabetes (type 1 or 2), it is essential to visit your ophthalmologist regularly to protect your vision. If you experience diabetic eye problems and seek solutions, visit us at Advanced Sight Center. Our board-certified ophthalmologists can offer you comprehensive care for your diabetes-related vision issues. We also offer care to prevent eye complications associated with diabetes.
To make an appointment with an experienced eye doctor, contact us today by calling our Washington office at (636) 239-1650, or fill out our appointment request form.
We look forward to helping to preserve or improve your vision!




